Sign and Verify Messages with HMAC Using the Web Crypto API
Web Crypto is a cryptography API available in modern browsers and Cloudflare Workers that can be used to sign messages and verify message signatures using Hashed-Based Message Authentication Codes (HMAC). This post provides an example implementation of signing and verifying using Cloudflare Workers.
Web Crypto
Web Crypto is a low level API for performing cryptographic functions such as encryption, decryption, and signature verification. The API is a W3C recommendation and some of the better documentation can be found on MDN.
Cloudflare Workers has native support of most of the Web Crypto API. The details are listed in their documentation.
Hashed-Based Message Authentication Code (HMAC)
HMAC is a hashing function that can be used as a way to sign and verify messages to ensure authenticity and is described in RFC2104.
In typical usage, a shared key is used generate a signature of a message. The signature is provided along with the message by the sender. The receiver uses their copy of the shared secret to verify the signature provided is valid to know whether or not to trust the message.
Verifying HMAC Signatures with Cloudflare Workers
In this sample scenario we're going to create a sample Cloudflare Worker that provides two main services:
- GET -> reply with an HTTP response header set to the signature for the text provided as a query string
- POST -> check the validity of base64 signature provided as an HTTP header for message in the HTTP body
We'll start by defining our shared secret. For a real life implementation, you'd want to configure this as a Worker Secret instead of hard coding the value.
const SECRET = "SECRET_KEY";
Web Crypto's sign and verify methods require a crypto key as input, so we'll create a function to provide one based on the shared secret using the importKey method, which has the format:
const result = crypto.subtle.importKey(
format,
keyData,
algorithm,
extractable,
usages
);
The raw format will be used and the keyData will be the shared secret encoded as an Uint8Array. Extractable will be set to false and usages should allow the key to be used for both signing and verifying.
Based on this criteria, here is our importKey function:
async function importKey(secret) {
return await crypto.subtle.importKey(
'raw',
new TextEncoder().encode(secret),
{ name: 'HMAC', hash: 'SHA-256' },
false,
['sign', 'verify'],
)
}
A function called signResponse will be used for deriving signatures. Our function will accept a message as string and secret as string and respond with the HMAC signature for the message in base64 format. The function will use the Web Crypto sign method to create the signature, which has the following syntax:
const signature = crypto.subtle.sign(algorithm, key, data);
We'll use the previously defined importKey function to derive the key. Since the message is a string and the input data needs to be an ArrayBuffer, we'll once again use a TextEncoder to convert the type.
async function signResponse(message, secret) {
const key = await importKey(secret)
const signature = await crypto.subtle.sign(
'HMAC',
key,
new TextEncoder().encode(message),
)
// Convert ArrayBuffer to Base64
return btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(signature)))
}
For signature verification, we'll use the verify Web Crypto method:
const result = crypto.subtle.verify(algorithm, key, signature, data);
The verifySignature will take in a message as string, signature as a base64 string, and a secret as string. It will return a Promise for a boolean.
async function verifySignature(message, signature, secret) {
const key = await importKey(secret)
// Convert Base64 to Uint8Array
const sigBuf = Uint8Array.from(atob(signature), c => c.charCodeAt(0))
return await crypto.subtle.verify(
'HMAC',
key,
sigBuf,
new TextEncoder().encode(message),
)
}
Run Example in the Workers Playground
Click here to preview a fully functioning version of this sample in the Workers Playground.
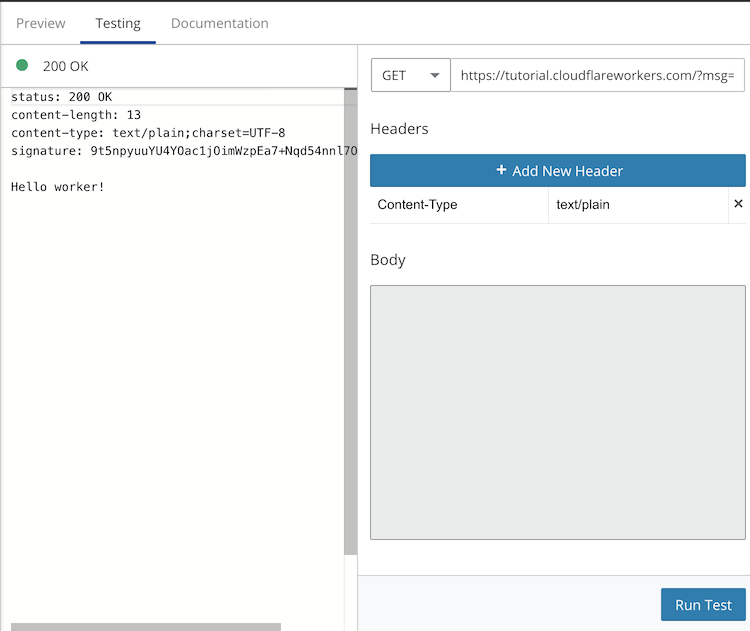
After opening the preview of this project, switch to the Testing tab on the right to run the sample. To test signing, submit a GET request with a query string msg set to any text value, for example Hello worker!. You'll get a response with an HTTP header containing the signature for that message.
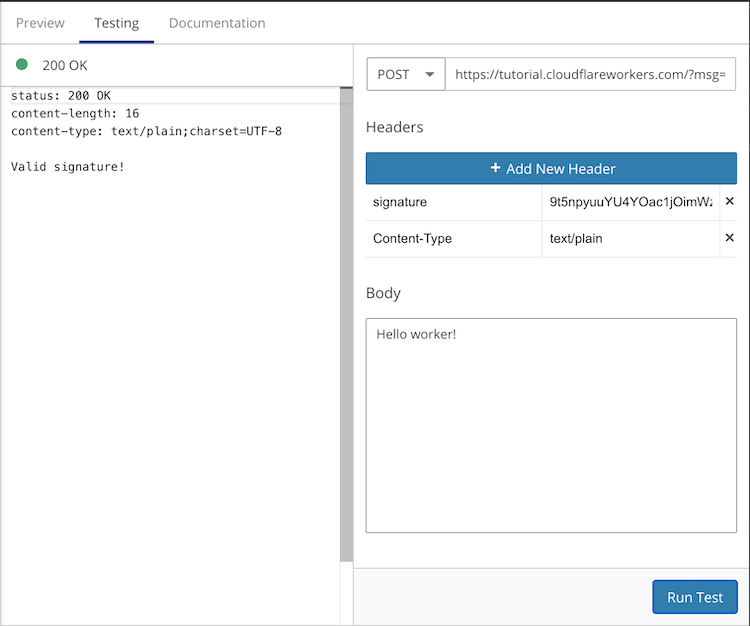
To test verifying, copy the provided signature from the GET request, switch the request method to POST and click the Add New Header button. Add a new header with the key signature and paste in the copied signature as the value. In the Body section paste the same message as before, i.e. Hello worker! and run the test. You should see an HTTP 200 OK response with Valid signature! as the body.
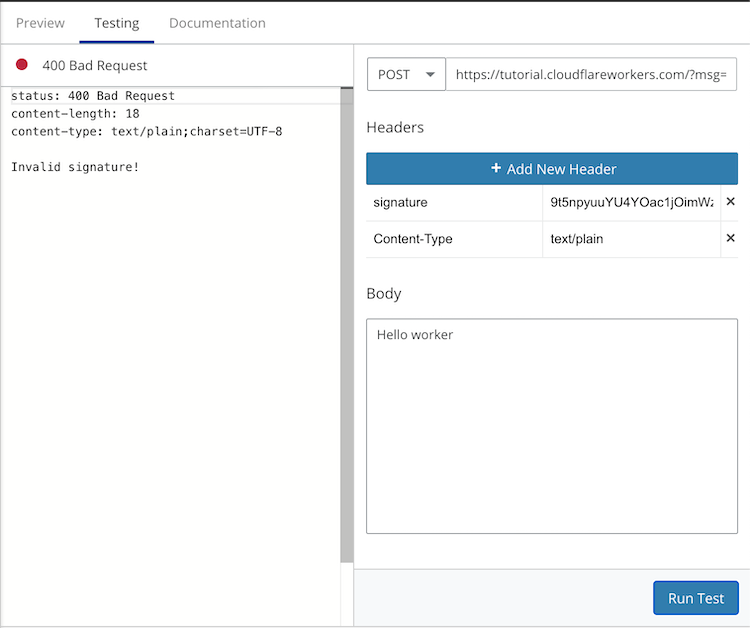
Play around with different messages and signatures to check that the Worker is properly validating the signatures. For example, modifying the body by removing the ! in Hello worker! results in a 400 error with the response body stating the signature is invalid.
Full Source Code
const SECRET = 'SECRET_KEY'
addEventListener('fetch', event => {
event.respondWith(handleRequest(event.request))
})
async function handleRequest(request) {
if (request.method === 'GET') {
const url = new URL(request.url)
const msg = url.searchParams.get('msg') || ''
const signature = await signResponse(msg, SECRET)
let response = new Response(msg)
response.headers.set('signature', signature)
return response
} else if (request.method === 'POST') {
const message = await request.text()
const signature = request.headers.get('signature') || ''
const isSigValid = await verifySignature(message, signature, SECRET)
return isSigValid
? new Response('Valid signature!')
: new Response('Invalid signature!', { status: 400 })
} else {
return new Response('Method not supported')
}
}
async function importKey(secret) {
return await crypto.subtle.importKey(
'raw',
new TextEncoder().encode(secret),
{ name: 'HMAC', hash: 'SHA-256' },
false,
['sign', 'verify'],
)
}
async function signResponse(message, secret) {
const key = await importKey(secret)
const signature = await crypto.subtle.sign(
'HMAC',
key,
new TextEncoder().encode(message),
)
// Convert ArrayBuffer to Base64
return btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(signature)))
}
async function verifySignature(message, signature, secret) {
const key = await importKey(secret)
// Convert Base64 to Uint8Array
const sigBuf = Uint8Array.from(atob(signature), c => c.charCodeAt(0))
return await crypto.subtle.verify(
'HMAC',
key,
sigBuf,
new TextEncoder().encode(message),
)
}